Rasa
Rasa, pengamatan gustatori, or pengecapan[1] merupakan salah satu dari lima deria tradisional. Rasa merupakan sensasi yang dihasilkan apabila sesuatu bahan dalam mulut bertindak balas secara kimia dengan deria penerima kudup rasa.
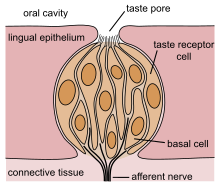
Rasa bersama dengan bau (olfaction) dan ransangan saraf trigeminal (dengan sentuhan bagi tekstur, juga sakit, dan suhu), menentukan perisa, dan gambaran deria bagi makanan atau bahan lain.
Manusia mendapat rasa melalui organ deria yang dikenali sebagai kudup rasa,[2] atau gustatory calyculi, tertumpu pada atas lidah.[3] Terdapat sekitar 100,000 kudup rasa yang terletak di belakang dan hadapan lidah. Yang lain terletak di lelangit, sisi dan belakang mulut, dan di tekak.
Sensasi rasa dalam bangsa Melayu boleh dikelaskan pada beberapa rasa asas: manis, pahit, masam, masin, pedas, maung[4], pedar, lemak[5] dan umami. Media rasa mampu membezakan antara rasa berbeza melalui interaksi dengan molekul berbeza atau ion. rasa manis, umami, dan pahit dipicu oleh ikatan molekul pada penerima pasangan-protin G pada selaput sel pada kudup rasa. Masin dan masam dirasai apabila logam alkali atau ion hidrogen memasuki kudup rasa, berturutan.[6]
Oleh kerana rasa mengesan kedua-dua bahan merbahaya dan berguna, kesemua rasa asas dikelaskan samaada memual atau menarik, bergantung pada kesan bahan yang ia kesan pada tubuh kita.[7] Rasa manis membantu mengenal pasti makanan kaya tenaga, sementara pahit bertindak sebagai tanda amaran racun.[8]
Rujukan
sunting- ^ Adjectival form: gustatory
- ^ What Are Taste Buds? kidshealth.org
- ^ Human biology (Page 201/464) Daniel D. Chiras. Jones & Bartlett Learning, 2005.
- ^ Growing Up in Trengganu By Awang Goneng
- ^ Dewan sastera, Volume 32, Issues 7-12, Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka, 2002
- ^ Human Physiology: An integrated approach 5th Edition -Silverthorn, Chapter-10, Page-354
- ^ Why do two great tastes sometimes not taste great together? scientificamerican.com. Dr. Tim Jacob, Cardiff University. May 22, 2009.
- ^ Miller, Greg (2). "Sweet here, salty there: Evidence of a taste map in the mammilian brain". Science. 333 (6047): 1213. doi:10.1126/science.333.6047.1213. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (bantuan); Check date values in:|date=dan|year=/|date=tidak padan (bantuan)
Bacaan lanjut
sunting- The Science of taste at Kitchen Geekery. An informative article about the science behind taste. Written from a culinary science perspective.
- Bartoshuk, Linda M (June 1978), "The Psychophysics of Taste" (PDF), American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 31 (6): 1068–1077, PMID 352127, dicapai pada 12 September 2010
- Chandrashekar, Jayaram; Hoon, Mark A; Ryba , Nicholas J. P. & Zuker, Charles S (16 November 2006), "The receptors and cells for mammalian taste" (PDF), Nature, 444 (7117): 288–294, doi:10.1038/nature05401, PMID 17108952, diarkibkan daripada yang asal (PDF) pada 2011-07-22, dicapai pada 13 September 2010CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Chaudhari, Nirupa & Roper, Stephen D (2010), "The cell biology of taste" (PDF), Journal of Cell Biology, 190 (3): 285–296, doi:10.1083/jcb.201003144, PMC 2922655, PMID 20696704, dicapai pada 13 September 2010CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Danker, W.H (1968), Basic Principles of Sensory Evaluation, Philadelphia: American Society for Testing and Materials, ISBN 978-0-8031-4572-6, dicapai pada 13 September 2010
- Dulac, Catherine (March 17, 2000), "The Physiology of Taste, Vintage 2000" (PDF), Cell, 100 (6): 607–610, doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80697-2, PMID 10761926, diarkibkan daripada yang asal (PDF) pada 2010-07-18, dicapai pada 13 September 2010
- Finger, Thomas E, penyunting (2009), International Symposium on Olfaction and Taste, Boston: Blackwell, for the New York Academy of Sciences, ISBN 1-57331-738-1, dicapai pada 12 September 2010 Alternative ISBN 978-1-57331-738-2
- Hui, Y.H, penyunting (2010), Handbook of Fruit and Vegetable Flavors, Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-470-22721-3, dicapai pada 13 September 2010 See especially comments and key references in regards tasteCS1 maint: postscript (link)
- Thomas Hummel & Antje Welge-Lüssen, penyunting (2006), Tast and Smell: An Update, Advances in Oto-Rhino-Laryngolog, Vol.63, Basel, Switzerland: Karger, ISBN 3-8055-8123-8, dicapai pada 12 September 2010
|volume=has extra text (bantuan) - Lawless, Harry T., & Heymann, Hildegarde (1998), Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices, New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, ISBN 0-8342-1752-X, dicapai pada 13 September 2010CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Macbeth, Helen, penyunting (2006), Food Preferences and Taste: Continuity and Change, The Anthropology of Food and Nutrition, Vol.2, Providence, Rhode Island: Berghahn Books, ISBN 1-57181-958-4, dicapai pada 12 September 2010
|volume=has extra text (bantuan) Paperback ISBN 1-57181-970-3 - Patton, Harry D (March 1950), "Physiology of Smell and Taste", Annual Review of Physiology, 12: 469–484, doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.12.030150.002345, PMID 15411178, dicapai pada 12 September 2010
- Reed, Danielle R; Tanaka, Toshiko; and McDaniel, Amanda H (June 30, 2006), "Diverse tastes: Genetics of sweet and bitter perception", Physiology & Behavior, 88 (3): 215–226, doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.05.033, PMC 1698869, PMID 16782140
|access-date=requires|url=(bantuan)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Reineccius, Gary, penyunting (1999), Source Book of Flavours (ed. 2nd), Gaithersburg, Maryland: Aspen, ISBN 0-8342-1307-9, dicapai pada 12 September 2010 Previously published 1994 by Chapman & Hall, New York ISBN 0-442-00376-5CS1 maint: postscript (link)
- Schiffman, Susan S (26 May 1983), "Taste and smell in disease (First of two parts)", The New England Journal of Medicine, 308 (21): 1275–1279.
- Schiffman, Susan S; Schiffman, Susan S. (2 June 1983), "Taste and smell in disease (Second of two parts)", The New England Journal of Medicine, 308 (22): 1337–1343, doi:10.1056/NEJM198306023082207, PMID 6341845.
- Schiffman, S.S (2000), "Taste and smell perception affect appetite and immunity in the elderly" (PDF), European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 54 (Suppl. 3): S54–S63, PMID 11041076, dicapai pada 16 June 2010. Unknown parameter
|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (bantuan) - Seiden, Allen M, penyunting (1997), Taste and Smell Disorders, Rhinology and Sinusology, New York: Thieme, ISBN 0-86577-533-8, dicapai pada 12 September 2010 Alternative ISBN 3-13-107261-X
- Shallenberger, R.S (1993), Taste Chemistry, London & New York: Blackie Academic & Professional (imprint of Chapman & Hall), ISBN 0-7514-0150-1, dicapai pada 12 September 2010
- Svrivastava, R.C. & Rastogi, R.P (2003), "Relative taste indices of some substances", dalam . (penyunting), Transport Mediated by Electrical Interfaces, Studies in interface science, vol.18, Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Science, ISBN 0-444-51453-8 B.V Check
|isbn=value: invalid character (bantuan), dicapai pada 12 September 2010 Taste indices of table 9, p.274 are select sample taken from table in Guyton's Textbook of Medical Physiology (present in all editions)|volume=has extra text (bantuan)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: editors list (link) CS1 maint: postscript (link) - Xiaodong Li, Lena Staszewski, Hong Xu, Kyle Durick, Mark Zoller, and Elliot Adler (April 2, 2002), "Human receptors for sweet and umami taste", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99 (7): 4692–4696, doi:10.1073/pnas.072090199, PMC 123709, PMID 11917125, dicapai pada 13 September 2010CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Pautan luar
sunting| Cari sour dalam Wikikamus bahasa Melayu, kamus bebas. |
| Wikimedia Commons mempunyai media berkaitan Rasa |
- Researchers Define Molecular Basis of Human "Sweet Tooth" and Umami Taste
- Statistics on Taste at National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. An informative overview with good list of references.
- The Science of taste at Kitchen Geekery. An informative article about the science behind taste. Written from a culinary science perspective.